Azure for Active Directory: 7 Ultimate Power Tips for 2024
Thinking about upgrading your identity management? Azure for Active Directory isn’t just a trend—it’s a game-changer. Discover how this powerhouse solution transforms security, scalability, and remote access with seamless cloud integration.
Understanding Azure for Active Directory: The Modern Identity Backbone

Azure for Active Directory, commonly known as Azure AD, is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service. It plays a pivotal role in enabling organizations to securely manage user identities, control access to applications, and streamline authentication across hybrid and cloud environments. Unlike traditional on-premises Active Directory, Azure AD is built for the cloud-first world, offering scalable, flexible, and resilient identity solutions.
What Is Azure Active Directory?
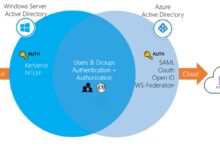
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is not simply a cloud version of Windows Server Active Directory. It’s a distinct service designed specifically for modern authentication protocols like OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and SAML. It enables single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conditional access policies across thousands of cloud and on-premises applications.
- Azure AD supports over 2,600 pre-integrated SaaS apps, including Salesforce, Dropbox, and Microsoft 365.
- It provides identity as a service (IDaaS), allowing organizations to offload identity management to the cloud.
- Unlike traditional AD, Azure AD uses REST APIs and JSON for communication, making it ideal for modern app development.
Key Differences Between On-Premises AD and Azure AD
While both systems manage identities, their architecture and use cases differ significantly. On-premises Active Directory relies on domain controllers, Group Policy, and LDAP, whereas Azure AD is API-driven and built around HTTP-based protocols.
- On-prem AD uses NTLM and Kerberos for authentication; Azure AD uses token-based authentication.
- Group Policy Objects (GPOs) are central to on-prem AD but not supported in Azure AD. Instead, Intune and endpoint management tools are used.
- Azure AD supports global scalability, while on-prem AD requires complex replication setups.
“Azure AD is not a replacement for on-prem AD—it’s an evolution.” — Microsoft Identity Documentation
Why Azure for Active Directory Is Essential for Modern Businesses
In today’s hybrid work environment, organizations need a robust identity solution that supports remote access, zero-trust security models, and seamless application integration. Azure for Active Directory delivers exactly that, making it a cornerstone of digital transformation strategies.
Support for Hybrid and Cloud-First Environments
With more companies adopting hybrid work models, the demand for cloud-based identity solutions has skyrocketed. Azure for Active Directory bridges the gap between on-premises infrastructure and cloud services through Azure AD Connect, which synchronizes user identities from on-prem AD to the cloud.
- Azure AD Connect enables password hash synchronization, pass-through authentication, and seamless SSO.
- It allows users to log in with the same credentials across cloud and on-prem apps.
- Hybrid identity reduces the need for complex VPN setups and improves user experience.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority for enterprises, and Azure for Active Directory offers advanced features like Identity Protection, Conditional Access, and Risk-Based Policies to detect and respond to threats in real time.
- Azure AD Identity Protection uses machine learning to detect risky sign-ins and user behavior.
- Conditional Access policies enforce rules such as requiring MFA for high-risk logins or blocking access from untrusted locations.
- Compliance reports and audit logs help organizations meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
Core Features of Azure for Active Directory You Can’t Ignore
Azure for Active Directory comes packed with powerful features that empower IT teams to manage identities efficiently while enhancing user productivity and security.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Across Applications
One of the most sought-after benefits of Azure for Active Directory is its ability to provide seamless single sign-on to thousands of cloud and on-premises applications.
- Users can access apps like Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and Zoom with one set of credentials.
- Administrators can configure SSO using SAML, OAuth, or password-based methods.
- SSO reduces password fatigue and improves user adoption of secure practices.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a critical layer of security that requires users to verify their identity using two or more methods—something they know (password), something they have (phone or token), or something they are (biometrics).
- Azure AD MFA supports phone calls, text messages, authenticator apps, and FIDO2 security keys.
- It can be enforced globally or based on risk level via Conditional Access policies.
- According to Microsoft, MFA blocks over 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
Conditional Access and Risk-Based Policies
Conditional Access is a powerful feature that allows administrators to define access rules based on user, device, location, application, and risk level.
- Policies can require MFA, device compliance, or approved client apps before granting access.
- Risk levels (low, medium, high) are calculated using AI-driven signals from sign-in attempts.
- Organizations can set up automatic remediation actions, such as blocking access or requiring password reset.
How Azure for Active Directory Integrates with Microsoft 365
Microsoft 365 and Azure for Active Directory are deeply integrated, making Azure AD the identity backbone for Office 365, Teams, SharePoint, and other productivity tools.
Seamless User Provisioning and Management
When you subscribe to Microsoft 365, Azure AD is automatically provisioned as the identity provider. This allows for centralized user management across all Microsoft services.
- Admins can create, update, or delete users in Azure AD, and changes sync across Microsoft 365 apps.
- Licensing is managed directly in Azure AD, ensuring users have the right access to tools like Exchange Online or Power BI.
- Dynamic groups in Azure AD can automatically assign licenses based on user attributes.
Secure Access to Microsoft 365 Apps
Azure for Active Directory ensures that only authorized users can access Microsoft 365 resources, even when working remotely.
- Conditional Access policies can restrict access to sensitive data from unmanaged devices.
- Session controls can limit download permissions or apply app protection policies.
- Integration with Microsoft Defender for Office 365 enhances email and collaboration security.
Implementing Azure for Active Directory: Step-by-Step Guide
Deploying Azure for Active Directory requires careful planning and execution. Whether you’re starting from scratch or migrating from on-premises AD, following a structured approach ensures success.
Planning Your Azure AD Deployment
Before implementation, assess your current environment, define your goals, and choose the right deployment model (cloud-only, hybrid, or staged migration).
- Identify which users and applications will be migrated first.
- Define naming conventions, group structures, and administrative roles.
- Review licensing requirements—Azure AD offers Free, Office 365 apps, P1, and P2 editions.
Setting Up Azure AD Connect
Azure AD Connect is the bridge between on-premises Active Directory and Azure AD. It synchronizes user accounts, groups, and passwords to the cloud.
- Download and install Azure AD Connect from the official Microsoft documentation.
- Choose synchronization options: password hash sync, pass-through authentication, or federation.
- Enable seamless SSO to allow users to authenticate without re-entering credentials.
Configuring Single Sign-On and MFA
Once identities are synchronized, configure SSO and MFA to enhance security and user experience.
- Register applications in Azure AD and configure SSO settings.
- Enforce MFA for all users or specific groups via the Security > MFA section.
- Use the Azure AD portal to monitor sign-in activity and troubleshoot issues.
Advanced Capabilities: Azure for Active Directory and Identity Governance
Beyond basic authentication, Azure for Active Directory offers advanced identity governance features that help organizations manage access at scale.
Access Reviews and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Access reviews allow administrators to periodically verify who has access to which resources, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of privilege creep.
- Set up automated access reviews for apps, groups, or Azure roles.
- Integrate with Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for just-in-time (JIT) access.
- RBAC enables fine-grained control over who can perform specific actions in Azure and Microsoft 365.
Entitlement Management and Identity Lifecycle
Entitlement management allows organizations to create access packages that bundle resources for specific roles or projects.
- Users can request access through a self-service portal.
- Approvals can be routed to managers or compliance teams.
- Access expires automatically, reducing the risk of stale permissions.
Common Challenges and Best Practices for Azure for Active Directory
While Azure for Active Directory offers immense benefits, organizations often face challenges during implementation and ongoing management.
Overcoming Synchronization Issues
Azure AD Connect synchronization failures can lead to login problems and access issues.
- Regularly monitor sync health using the Synchronization Service Manager.
- Resolve attribute conflicts and duplicate object errors promptly.
- Use filtering to exclude unnecessary OUs or objects from synchronization.
Managing User Adoption and Training
Users may resist changes like MFA or new login processes. Effective communication and training are key.
- Provide clear guides on how to set up the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Run pilot programs before full rollout.
- Use Azure AD’s built-in usage reports to identify inactive users or apps.
Security Best Practices for Azure AD
Securing Azure AD is critical, as it’s the gateway to your organization’s digital assets.
- Enable MFA for all users, especially administrators.
- Use PIM to manage privileged roles with time-bound activation.
- Regularly review audit logs and sign-in reports for suspicious activity.
- Implement Conditional Access policies to enforce device compliance and location-based access.
Future of Identity: Azure for Active Directory and Beyond
The identity landscape is evolving rapidly, and Azure for Active Directory continues to lead with innovations in passwordless authentication, AI-driven security, and decentralized identity.
Passwordless Authentication with FIDO2 and Windows Hello
Azure AD supports passwordless sign-in using FIDO2 security keys, Windows Hello, and the Microsoft Authenticator app.
- Users can log in using biometrics or physical keys instead of passwords.
- Passwordless reduces phishing risks and improves user experience.
- Organizations can enforce passwordless policies via Conditional Access.
AI and Machine Learning in Identity Protection
Azure AD Identity Protection leverages AI to detect anomalies and prevent breaches before they happen.
- Machine learning models analyze sign-in patterns, device health, and IP reputation.
- Risk detections trigger automated responses like MFA prompts or account blocks.
- Continuous improvement ensures the system adapts to new threats.
Integration with Zero Trust Security Models
Azure for Active Directory is a foundational component of Microsoft’s Zero Trust architecture.
- Zero Trust assumes no user or device is trusted by default, even inside the network.
- Azure AD enforces strict identity verification and least-privilege access.
- Integration with Microsoft Defender, Intune, and Azure Firewall creates a comprehensive security posture.
What is Azure for Active Directory?
Azure for Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service that enables secure user authentication and authorization across cloud and on-premises applications. It supports SSO, MFA, conditional access, and identity governance.
How does Azure AD differ from on-premises Active Directory?
On-premises AD uses domain controllers and LDAP for authentication, while Azure AD is cloud-native and uses token-based protocols like OAuth and OpenID Connect. Azure AD supports modern app development, global scalability, and advanced security features not available in traditional AD.
Can Azure AD replace on-premises Active Directory?
Azure AD can complement or partially replace on-prem AD, but many organizations use both in a hybrid model. Azure AD Connect synchronizes identities between the two. Full replacement is possible but requires careful planning and application compatibility checks.
What are the licensing options for Azure for Active Directory?
Azure AD offers four editions: Free, Office 365 apps, Premium P1, and Premium P2. The Free edition includes basic SSO and MFA, while P1 and P2 add Conditional Access, Identity Protection, and advanced governance features. Licensing is typically included with Microsoft 365 subscriptions.
How secure is Azure for Active Directory?
Azure AD is highly secure, featuring MFA, Conditional Access, Identity Protection, and continuous monitoring. Microsoft invests heavily in security and compliance, with Azure AD meeting standards like ISO 27001, SOC 1/2, and GDPR. When configured properly, it significantly reduces the risk of identity-based attacks.
Adopting Azure for Active Directory is no longer optional—it’s essential for modern enterprises. From enabling secure remote work to supporting zero-trust security models, Azure for Active Directory provides the foundation for a resilient, scalable, and future-ready identity strategy. By leveraging its powerful features like SSO, MFA, Conditional Access, and identity governance, organizations can enhance security, improve user experience, and stay compliant in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or optimizing an existing setup, Azure for Active Directory offers the tools and flexibility to succeed.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: