Azure Standard: 7 Powerful Insights You Must Know in 2024
Cloud computing has reshaped how businesses operate, and at the heart of this revolution is Microsoft Azure. Among its many service tiers, the Azure Standard stands out as a go-to choice for enterprises seeking reliability, scalability, and performance. But what exactly makes Azure Standard so essential? Let’s dive deep into its features, benefits, and real-world applications.
Understanding Azure Standard: The Foundation of Cloud Flexibility

The term Azure Standard refers to a tier of services within Microsoft Azure that balances performance, availability, and cost. Unlike the Basic tier, which is designed for lightweight workloads, the Azure Standard tier is built for production environments that demand high availability, redundancy, and enterprise-grade support. It covers a wide range of services—from virtual machines and storage to networking and databases—each optimized for scalability and resilience.
What Defines the Azure Standard Tier?
The Azure Standard tier is not a single product but a classification applied across multiple Azure services. For example, Azure Virtual Machines in the Standard tier offer guaranteed performance, SLA-backed uptime (typically 99.9%), and integration with Azure’s global infrastructure. This tier ensures that your applications run smoothly, even under heavy load.
- Guaranteed service level agreements (SLAs)
- High availability and redundancy options
- Support for enterprise-grade security and compliance
How Azure Standard Differs from Basic and Premium Tiers
Microsoft Azure offers three primary service tiers: Basic, Standard, and Premium. The Azure Standard tier sits in the middle, providing a balanced mix of performance and cost. While the Basic tier lacks features like load balancing and auto-scaling, the Standard tier includes them by default. On the other hand, the Premium tier offers enhanced performance and lower latency but at a significantly higher cost.
“The Azure Standard tier is where most production workloads live—it’s the sweet spot between cost and capability.” — Microsoft Azure Architect Guide
Azure Standard Virtual Machines: Powering Enterprise Workloads
One of the most widely used components under the Azure Standard umbrella is the Azure Virtual Machine (VM). These VMs are designed for applications that require consistent performance, such as web servers, application backends, and enterprise databases. They come in various sizes, from small (A-series) to memory-optimized (M-series) and compute-intensive (F-series).
Key Features of Azure Standard VMs
Azure Standard VMs are engineered for reliability and performance. They support advanced networking features like accelerated networking, IPv6, and network security groups. Additionally, they integrate seamlessly with Azure Backup, Azure Site Recovery, and Azure Monitor for comprehensive management.
- SLA of 99.9% uptime when deployed in availability sets
- Support for both Windows and Linux operating systems
- Integration with Azure Disk Encryption for data security
Use Cases for Azure Standard VMs
Organizations use Azure Standard VMs for a variety of critical applications. For example, a financial institution might run its core banking application on a Dv3-series VM, while a media company could use a G-series VM for video rendering. These VMs are also ideal for hybrid cloud setups, where on-premises systems connect to Azure via ExpressRoute or VPN Gateway.
Azure Standard Storage: Reliable and Scalable Data Management
Data is the lifeblood of modern applications, and Azure Standard storage provides a robust solution for storing and managing it. Azure offers several storage options under the Standard tier, including Blob Storage, File Storage, Queue Storage, and Table Storage. Each is designed for specific use cases, from unstructured data to structured NoSQL storage.
Types of Azure Standard Storage
Azure Standard storage comes in different forms, each optimized for performance and cost. Azure Blob Storage is ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data like images, videos, and backups. File Storage provides SMB-based file shares, perfect for legacy applications that require shared drives. Queue Storage enables asynchronous communication between services, while Table Storage offers a NoSQL key-value store.
- Blob Storage: For unstructured data like media files
- File Storage: For shared file systems and legacy apps
- Queue Storage: For message-based communication
Performance and Redundancy Options
Azure Standard storage offers multiple redundancy options to ensure data durability and availability. These include Locally Redundant Storage (LRS), Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS), Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS), and Read-Access Geo-Redundant Storage (RA-GRS). GRS, for instance, replicates data across two regions, providing protection against regional outages.
“With Azure Standard storage, you’re not just storing data—you’re future-proofing it.” — Azure Storage Documentation
Azure Standard Networking: Building Secure and Scalable Connections
Networking is a critical component of any cloud deployment, and the Azure Standard tier offers a comprehensive suite of networking services. These include Virtual Networks (VNet), Load Balancers, Application Gateways, and Azure DNS. Together, they enable secure, high-performance connectivity between cloud resources and on-premises systems.
Core Components of Azure Standard Networking
Azure Virtual Network allows you to create isolated environments in the cloud, similar to on-premises networks. You can define subnets, IP ranges, and routing rules. The Standard Load Balancer distributes traffic across multiple VMs, ensuring high availability. Application Gateway provides layer 7 load balancing and supports SSL termination, making it ideal for web applications.
- Virtual Networks: Isolated cloud environments
- Standard Load Balancer: Traffic distribution with high availability
- Application Gateway: Layer 7 routing and SSL offloading
Security and Compliance in Azure Standard Networking
Security is built into every layer of Azure Standard networking. Network Security Groups (NSGs) act as firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic. Azure Firewall provides stateful inspection and threat intelligence. Additionally, Azure DDoS Protection Standard helps defend against distributed denial-of-service attacks, ensuring your applications remain accessible during attacks.
Azure Standard Databases: Enterprise-Grade Data Solutions
When it comes to data management, the Azure Standard tier offers powerful database solutions like Azure SQL Database, Azure Database for MySQL, and Azure Database for PostgreSQL. These managed services eliminate the need for manual patching, backups, and scaling, allowing developers to focus on building applications.
Azure SQL Database: The Flagship Relational Service
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering that provides high performance, scalability, and built-in intelligence. The Standard tier of Azure SQL Database offers predictable performance with service level objectives (SLOs) measured in DTUs (Database Transaction Units). It supports advanced features like automatic tuning, threat detection, and geo-replication.
- Automatic backups with 7-day retention
- Threat detection and vulnerability assessment
- Geo-replication for disaster recovery
MySQL and PostgreSQL in the Azure Standard Tier
Azure also offers managed versions of open-source databases under the Standard tier. Azure Database for MySQL and Azure Database for PostgreSQL provide enterprise-grade reliability with automated backups, patching, and monitoring. These are ideal for applications built on LAMP or modern web stacks.
Azure Standard Pricing and Cost Management
One of the biggest advantages of the Azure Standard tier is its predictable pricing model. Unlike pay-as-you-go models that can lead to unexpected bills, Azure Standard services often come with transparent pricing based on usage, instance size, and region. However, without proper management, costs can still spiral out of control.
How Azure Standard Pricing Works
Pricing for Azure Standard services varies by service type. For example, a Standard_D2s_v3 VM costs more than a Standard_A2_v2 due to higher CPU and memory specs. Similarly, storage costs depend on the amount of data stored, redundancy option, and access frequency. Microsoft provides a Pricing Calculator to help estimate costs before deployment.
- Compute: Billed per second or per hour based on VM size
- Storage: Based on capacity, redundancy, and transaction volume
- Networking: Data transfer and bandwidth usage fees apply
Tools for Cost Optimization
Azure offers several tools to help manage and optimize costs. Azure Cost Management + Billing provides detailed reports and budget alerts. Reserved Instances allow you to commit to 1- or 3-year terms for up to 72% savings. Additionally, Azure Advisor recommends right-sizing underutilized VMs and deleting unused resources.
Azure Standard vs. Other Cloud Providers: A Competitive Edge
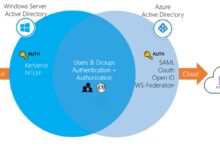
When comparing cloud platforms, the Azure Standard tier holds its own against offerings from AWS and Google Cloud. While AWS offers similar tiers (e.g., General Purpose Instances), Azure’s integration with Microsoft 365, Active Directory, and hybrid cloud tools gives it a unique advantage for enterprises already in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Feature Comparison: Azure vs. AWS vs. GCP
Azure Standard VMs offer comparable performance to AWS EC2’s General Purpose (M5) instances and Google Cloud’s N2 series. However, Azure stands out with its hybrid capabilities via Azure Arc and Azure Stack. This allows organizations to manage on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud resources from a single control plane.
- Azure: Strong hybrid and enterprise integration
- AWS: Broadest service catalog and global reach
- GCP: Superior data analytics and AI/ML tools
Why Enterprises Choose Azure Standard
Enterprises often choose Azure Standard because of its seamless integration with existing Microsoft tools, robust compliance certifications (like ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR), and global infrastructure. Additionally, Azure’s commitment to sustainability—with a goal of being carbon negative by 2030—resonates with organizations focused on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
Best Practices for Deploying Azure Standard Services
Deploying Azure Standard services effectively requires planning, monitoring, and optimization. Following best practices ensures high performance, security, and cost efficiency. Whether you’re launching a new application or migrating from on-premises, these guidelines will help you succeed.
Design for High Availability
Always deploy critical workloads in availability sets or availability zones to protect against hardware failures. Use Azure Load Balancer to distribute traffic and enable auto-scaling to handle traffic spikes. For databases, enable geo-replication to ensure data remains accessible during regional outages.
Implement Security from the Start
Apply the principle of least privilege using Azure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). Enable Azure Security Center (now Microsoft Defender for Cloud) to monitor threats and vulnerabilities. Use Azure Key Vault to manage secrets, certificates, and encryption keys securely.
Monitor and Optimize Performance
Leverage Azure Monitor and Application Insights to track application performance and diagnose issues. Set up alerts for CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk latency. Regularly review Azure Advisor recommendations to optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
What is Azure Standard?
Azure Standard refers to a tier of Microsoft Azure services designed for production workloads that require high availability, scalability, and enterprise-grade support. It includes virtual machines, storage, databases, and networking services with SLA-backed uptime and advanced features.
How does Azure Standard differ from Basic and Premium?
The Azure Standard tier offers a balance between cost and performance. Unlike the Basic tier, it includes load balancing and auto-scaling. Compared to the Premium tier, it provides slightly lower performance but at a more affordable price, making it ideal for most enterprise applications.
Is Azure Standard suitable for production environments?
Yes, Azure Standard is specifically designed for production workloads. It offers 99.9% SLA for virtual machines, automated backups, threat detection, and high availability features, making it a reliable choice for mission-critical applications.
How can I reduce costs on Azure Standard services?
You can reduce costs by using Reserved Instances, right-sizing underutilized resources, enabling auto-shutdown for non-production VMs, and leveraging Azure Cost Management tools to monitor spending and set budgets.
Can I migrate from Basic to Azure Standard easily?
Yes, migrating from Basic to Azure Standard is straightforward. You can redeploy your resources with Standard-tier configurations or use Azure Migrate to assess and move workloads seamlessly with minimal downtime.
The Azure Standard tier is more than just a service category—it’s a strategic choice for businesses aiming for reliability, scalability, and integration within the Microsoft ecosystem. From virtual machines and storage to databases and networking, Azure Standard delivers enterprise-grade capabilities with predictable pricing and robust support. By understanding its features, comparing it with competitors, and following best practices, organizations can maximize their cloud investments and drive innovation. Whether you’re just starting your cloud journey or optimizing an existing setup, Azure Standard offers the tools and infrastructure to succeed in today’s digital landscape.
Further Reading: