Sign In to Azure Portal: 7 Proven Steps for Instant Access
Want to sign in to Azure portal quickly and securely? Whether you’re a cloud beginner or an IT pro, this guide walks you through every step with clarity and precision.
Sign In to Azure Portal: Understanding the Basics

Before diving into the technical steps, it’s essential to understand what the Azure portal is and why signing in correctly matters. The Azure portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services, resources, and subscriptions. It acts as the central hub for deploying virtual machines, configuring networks, monitoring performance, and managing security settings across your cloud environment.
When you sign in to Azure portal, you’re not just accessing a dashboard — you’re entering a powerful ecosystem that connects to Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and hundreds of integrated SaaS applications. Your login determines your access level, permissions, and visibility within the tenant. That’s why authentication isn’t just about convenience — it’s a critical component of cloud security.
What Is the Azure Portal?
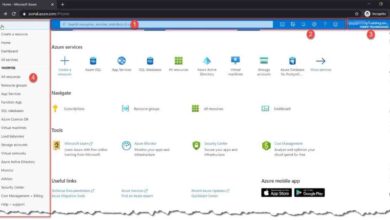
The Azure portal (portal.azure.com) is a unified console that allows users to interact with Microsoft Azure services through a graphical user interface. Unlike command-line tools like Azure CLI or PowerShell, the portal provides visual navigation, real-time monitoring, and guided setup wizards for complex tasks such as creating AI models or setting up hybrid cloud environments.
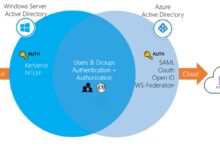
It supports role-based access control (RBAC), resource grouping, cost management dashboards, and integration with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). This makes it indispensable for administrators, developers, and finance teams who need to oversee cloud usage and compliance.
Why Signing In Correctly Matters
Incorrect login procedures can lead to authentication failures, locked accounts, or even unauthorized access if credentials are compromised. For example, using a personal Microsoft account when your organization uses Azure AD can result in being directed to the wrong tenant, limiting your ability to manage corporate resources.
Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA) requirements may vary depending on your organization’s security policies. Failing to meet these during the sign-in process will block access, even with correct credentials. Therefore, knowing how to properly sign in to Azure portal ensures productivity and compliance.
“Authentication is the first line of defense in cloud security. A secure sign-in process protects data, prevents breaches, and ensures only authorized users access critical systems.” — Microsoft Security Best Practices
Step-by-Step Guide to Sign In to Azure Portal
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals, let’s walk through the actual process of logging into the Azure portal. This section provides a detailed, step-by-step breakdown suitable for both new and experienced users.
Navigate to the Official Azure Portal URL
The first step is to go to the correct website: https://portal.azure.com. Always ensure you’re visiting the official domain to avoid phishing attacks. Fake login pages often mimic the real one but use slight variations in the URL (e.g., azure-login.com).
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Using a bookmarked link or typing the address manually reduces the risk of landing on a malicious site. If your organization has a custom domain for Azure access, your IT department should provide that instead.
Enter Your Work or School Account Email
On the login screen, enter the email address associated with your Azure subscription. This is typically a work or school account (e.g., user@company.com), not a personal Outlook.com or Hotmail address — unless explicitly configured for Azure access.
If you’re unsure which account to use, check with your organization’s Azure administrator. They can confirm your assigned user identity and whether you have an active license for Azure services.
Authenticate with Password and MFA
After entering your email, click ‘Next’ and input your password. If multi-factor authentication is enabled — which it should be for security — you’ll be prompted to verify your identity via one of several methods:
- Microsoft Authenticator app notification
- Text message (SMS) code
- Phone call verification
- Hardware security key (e.g., YubiKey)
Complete the challenge to proceed. Once authenticated, you’ll be redirected to the Azure dashboard, where you can begin managing resources.
Common Issues When Trying to Sign In to Azure Portal
Even with the right credentials, users often encounter obstacles when attempting to sign in to Azure portal. These issues range from simple typos to deeper configuration problems. Identifying them early saves time and frustration.
Incorrect Username or Password Errors
This is the most frequent issue. Double-check that Caps Lock is off and that you’re using the correct email format. Some organizations use aliases, so verify the exact username with your IT team.
If you’ve forgotten your password, use the ‘Forgot password?’ link on the login page. This triggers a reset workflow that may require MFA verification or approval from an admin, depending on policy settings.
Account Locked or Disabled
Repeated failed attempts can trigger account lockout policies. Similarly, inactive accounts may be disabled automatically after a set period. In such cases, contact your Azure administrator to unlock or reactivate the account.
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Administrators can manage user status via the Azure AD portal under ‘Users > All users’. From there, they can reset passwords, enable accounts, or assign new licenses.
MFA Prompt Not Received
If you’re not receiving MFA prompts, check your registered contact methods in Azure AD. Ensure your phone number is correct and that the Microsoft Authenticator app is installed and synced.
Network issues, expired app registrations, or outdated authentication methods can prevent MFA delivery. Users should periodically review their security info at https://mysignins.microsoft.com/security-info.
Using Different Account Types to Sign In to Azure Portal
Not all accounts are created equal when it comes to Azure access. Understanding the differences between account types helps avoid confusion during the login process.
Work or School Accounts (Azure AD)
These are managed identities within an organization’s Azure Active Directory tenant. They support single sign-on (SSO), conditional access policies, and centralized administration. Most enterprise users will use this type to sign in to Azure portal.
These accounts are provisioned by administrators and tied to specific roles and permissions. They cannot be created freely like personal accounts.
Microsoft Personal Accounts
Also known as Microsoft accounts (MSA), these include Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, or Live.com emails. While they can be used to create free Azure subscriptions, they lack enterprise-grade management features.
Personal accounts are ideal for individual developers or students experimenting with Azure. However, they should not be used in production environments due to limited governance controls.
Guest Accounts (B2B Collaboration)
Organizations often invite external partners as guest users through Azure AD B2B collaboration. These users retain their home tenant credentials but gain limited access to the host Azure environment.
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
When a guest signs in, they authenticate through their own organization’s identity provider. This maintains security while enabling cross-company collaboration.
Security Best Practices After You Sign In to Azure Portal
Signing in is just the beginning. Once inside, it’s crucial to follow security best practices to protect your environment from threats.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds a second layer of verification beyond passwords. Even if credentials are stolen, attackers cannot access your account without the second factor.
Organizations should enforce MFA through Conditional Access policies in Azure AD. Users can manage their MFA settings at https://account.activedirectory.windowsazure.com.
Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Rather than granting full administrative rights, assign users the minimum permissions they need. Azure’s RBAC model includes built-in roles like ‘Reader’, ‘Contributor’, and ‘Virtual Machine Administrator’.
Custom roles can also be defined for granular control. This principle of least privilege reduces the risk of accidental deletions or malicious actions.
Monitor Sign-In Activity Regularly
Azure AD provides detailed sign-in logs under ‘Monitoring > Sign-ins’. Review these logs to detect suspicious activity, such as logins from unfamiliar locations or devices.
You can set up alerts for risky sign-ins using Azure AD Identity Protection, which leverages AI to flag anomalies based on user behavior and device health.
Advanced Authentication Methods for Signing In
Beyond passwords and MFA, Azure supports modern authentication techniques that enhance both security and user experience.
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Passwordless Authentication with Microsoft Authenticator
The Microsoft Authenticator app allows passwordless sign-ins using biometrics (fingerprint or face recognition). After initial setup, users approve login requests directly from their mobile device.
This eliminates the risk of password theft and phishing. To enable it, go to ‘My Security Info’ and add the Authenticator app as a sign-in method.
FIDO2 Security Keys
FIDO2-compliant hardware keys (like YubiKey) offer phishing-resistant authentication. They work by generating cryptographic signatures that verify the user’s identity without transmitting secrets.
These keys are ideal for high-security environments and can be enforced via Conditional Access policies in Azure AD.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration
Enterprises often integrate Azure AD with on-premises identity providers (e.g., Active Directory Federation Services) or third-party SSO solutions like Okta or Ping Identity.
SSO allows users to access multiple applications — including the Azure portal — with one login, improving usability while maintaining centralized control.
Troubleshooting Tips: What to Do If You Can’t Sign In to Azure Portal
Despite best efforts, login issues persist. This section offers actionable troubleshooting steps to regain access.
Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
Stored data can interfere with authentication flows. Clear your browser’s cache, cookies, and site data for portal.azure.com. Try using an InPrivate or Incognito window to rule out extension conflicts.
Supported browsers include Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari. Avoid outdated versions or unsupported browsers like Internet Explorer.
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Try a Different Device or Network
Network restrictions (e.g., firewalls, proxies) may block authentication endpoints. Switching to a different network (like mobile hotspot) can help isolate the issue.
Similarly, testing on another device confirms whether the problem is local or account-wide.
Contact Your Azure Administrator
If all else fails, reach out to your organization’s Azure admin. They can check your account status, reset credentials, or adjust Conditional Access policies that might be blocking your login.
Admins can also use the Azure portal to simulate sign-in failures and diagnose root causes using diagnostic tools under ‘Azure AD > Sign-in logs’.
Optimizing Your Experience After You Sign In to Azure Portal
Once logged in, you can customize your workspace for better efficiency and faster navigation.
Personalize the Dashboard
The Azure dashboard is fully customizable. Pin frequently used resources, create resource groups, and arrange tiles for quick access.
You can save multiple dashboards for different roles (e.g., DevOps, Finance, Security) and switch between them easily.
Use Azure Cloud Shell
Available directly in the portal, Azure Cloud Shell provides a browser-based command line for running PowerShell or Bash scripts. It’s pre-authenticated, so you don’t need to log in again.
Cloud Shell is useful for automating tasks, managing resources at scale, and troubleshooting issues without leaving the browser.
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Leverage Quickstart Templates
Azure offers hundreds of deployment templates to speed up resource creation. Found under ‘Create a resource > Templates’, these pre-built configurations reduce manual errors and ensure consistency.
You can also save your own templates for reuse across environments.
How do I reset my Azure portal password?
If you’ve forgotten your password, click ‘Forgot password?’ on the login screen. Follow the prompts to verify your identity and set a new password. If MFA is required, you’ll need access to your registered device or method.
Can I use a personal Microsoft account to sign in to Azure portal?
Yes, but only if you’ve created a free Azure subscription with that account. For organizational use, a work or school account (Azure AD) is recommended for better management and security.
Why am I being asked to verify my identity every time I sign in?
This could be due to Conditional Access policies requiring MFA for every login, or your session settings expiring quickly. Check with your admin to adjust sign-in frequency rules.
What should I do if I’m locked out of my Azure account?
sign in to azure portal – Sign in to azure portal menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Contact your Azure administrator immediately. They can unlock your account, reset your password, or adjust policies that may be causing the block.
Is it safe to sign in to Azure portal from public Wi-Fi?
While technically possible, it’s not recommended. Public networks are vulnerable to eavesdropping. Always use a trusted network or a virtual private network (VPN) when accessing sensitive systems like Azure.
Successfully signing in to the Azure portal is the gateway to managing your cloud infrastructure. By following the correct procedures, understanding account types, and applying security best practices, you can ensure smooth and secure access. Whether you’re troubleshooting login issues or optimizing your dashboard, this guide equips you with the knowledge to navigate Azure confidently.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: