Azure Apps: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Looking to scale your applications with cloud power? Azure apps offer unmatched flexibility, security, and integration for modern businesses.
What Are Azure Apps and Why They Matter

Microsoft Azure apps refer to a broad category of cloud-based applications and services hosted on the Azure platform. These applications can range from simple web apps to complex enterprise-grade solutions leveraging AI, IoT, and machine learning. Azure apps are built using Azure App Service, a fully managed platform that enables developers to create, deploy, and scale web and mobile applications quickly and securely.
Defining Azure App Service
Azure App Service is the backbone of most Azure apps. It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks such as .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and PHP. This flexibility allows developers to deploy applications without worrying about infrastructure management. Microsoft provides automatic scaling, built-in security features, and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
- Supports Windows and Linux environments
- Enables deployment from GitHub, Azure DevOps, or Bitbucket
- Offers staging slots for testing before production rollout
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, Azure App Service is designed for high availability and global scalability, making it ideal for enterprise applications (Learn more on Microsoft Learn).
Types of Applications Supported
Azure apps aren’t limited to websites. The platform supports various application types including:
- Web Apps – for hosting websites and web APIs
- Mobile Apps – backend services for iOS, Android, and Windows apps
- API Apps – to expose business logic via RESTful APIs
- Logic Apps – for automating workflows across cloud services
This versatility makes Azure a go-to platform for full-stack development in hybrid and cloud-native environments.
“Azure App Service enables developers to focus on code, not infrastructure.” – Microsoft Azure Documentation
Core Features of Azure Apps
Azure apps come packed with features that empower developers and IT teams to build resilient, scalable, and secure applications. These features are designed to reduce operational overhead while maximizing performance and reliability.
Auto-Scaling and Load Balancing
One of the most powerful features of Azure apps is auto-scaling. Based on traffic demand, Azure can automatically increase or decrease the number of instances running your application. This ensures optimal performance during peak loads and cost efficiency during low-traffic periods.
- Scale based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics
- Set schedules for predictable traffic patterns (e.g., business hours)
- Use Azure Monitor to track performance and trigger scaling rules
This dynamic scaling is crucial for e-commerce platforms, SaaS products, and event-driven applications that experience variable user loads.
Integrated DevOps and CI/CD
Azure apps seamlessly integrate with DevOps tools. Developers can set up CI/CD pipelines using Azure Pipelines, GitHub Actions, or Jenkins. This allows for automated testing, staging, and deployment across environments.
- Deploy from any Git repository
- Use deployment slots to test changes in isolation
- Perform zero-downtime deployments with slot swapping
For teams practicing agile development, this integration reduces time-to-market and improves release quality.
Security and Compliance in Azure Apps
Security is a top priority for any cloud application, and Azure apps are no exception. Microsoft invests heavily in securing its cloud infrastructure, offering enterprise-grade protection for data and applications.
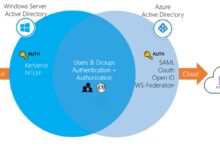
Built-in Authentication and Authorization
Azure App Service includes built-in authentication (Easy Auth) that supports identity providers like Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), Facebook, Google, Microsoft Account, and Twitter. This allows developers to implement secure login systems without writing custom code.
- Enable single sign-on (SSO) across applications
- Integrate with Azure AD for enterprise identity management
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to manage user permissions
This feature is especially useful for internal business apps that require secure employee access.
Data Encryption and Compliance Standards
All data in transit and at rest is encrypted by default in Azure apps. Microsoft complies with global standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2. This makes Azure a trusted platform for healthcare, finance, and government applications.
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for databases
- SSL/TLS for secure communication
- Private endpoints to isolate traffic within a virtual network
Organizations can also use Azure Security Center to monitor threats and receive recommendations for improving security posture.
“Azure meets more compliance standards than any other cloud provider.” – Microsoft Trust Center
Integration Capabilities of Azure Apps
Azure apps are designed to work seamlessly with other Azure services and third-party platforms. This integration capability is a key reason why enterprises choose Azure for digital transformation.
Connecting with Azure Databases
Azure apps can easily connect to various database services such as Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. These databases are fully managed, offering high availability, automatic backups, and geo-replication.
- Use connection strings to link apps with databases
- Leverage Cosmos DB for globally distributed NoSQL data
- Enable hybrid scenarios with Azure Database for PostgreSQL
For example, a global e-commerce app can use Cosmos DB to ensure low-latency access to product data across regions.
Integration with Logic Apps and Power Platform
Azure Logic Apps enables workflow automation by connecting apps, data, and services. When combined with Power Automate and Power Apps, businesses can create powerful low-code solutions.
- Automate approval workflows from SharePoint to email
- Sync data between Salesforce and Azure SQL
- Trigger Azure Functions based on file uploads
This integration reduces manual work and improves operational efficiency across departments.
Cost Management and Pricing Models for Azure Apps
Understanding the cost structure of Azure apps is essential for budget planning and optimization. Azure offers flexible pricing models that cater to startups, SMBs, and large enterprises.
Pricing Tiers and Plans
Azure App Service offers several pricing tiers: Free, Shared, Basic, Standard, Premium, and Premium V2/V3. Each tier provides different levels of performance, scalability, and features.
- Free and Shared: Ideal for testing and small projects
- Standard: Includes auto-scaling and SSL
- Premium: Best for production workloads with high traffic
The Premium tier also supports virtual network integration, private endpoints, and faster SSD storage.
Cost Optimization Strategies
To avoid overspending, organizations should adopt cost optimization practices:
- Use Azure Cost Management + Billing to track usage
- Scale down during non-business hours
- Reserve instances for predictable workloads to save up to 65%
Additionally, Azure Advisor provides personalized recommendations for reducing costs while maintaining performance.
“With reserved instances, you can save significantly on long-term app hosting.” – Azure Pricing Guide
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Even the best-designed Azure apps require continuous monitoring to ensure reliability and performance. Azure provides robust tools to track application health and troubleshoot issues in real time.
Using Azure Monitor and Application Insights
Azure Monitor collects logs, metrics, and traces from Azure apps. Application Insights, a feature of Azure Monitor, provides deep insights into application performance, including response times, failure rates, and user behavior.
- Set up alerts for high CPU or memory usage
- Track custom events and exceptions in code
- Visualize performance with dashboards
For example, if an API endpoint starts responding slowly, Application Insights can pinpoint the exact function causing the delay.
Diagnosing Issues with Log Analytics
Log Analytics allows you to query and analyze log data using Kusto Query Language (KQL). This is invaluable for debugging complex issues.
- Search for error messages across multiple app instances
- Analyze traffic patterns during outages
- Create custom reports for IT teams
By combining logs from App Service, databases, and network components, teams can get a holistic view of system health.
Migrating to Azure Apps: Best Practices
Many organizations are moving from on-premises servers or other cloud platforms to Azure apps. A successful migration requires careful planning and execution.
Assessment and Planning Phase
Before migration, assess your current applications for compatibility with Azure. Use the Azure Migrate tool to discover on-premises servers, evaluate dependencies, and estimate costs.
- Identify applications that can be rehosted (lift-and-shift)
- Determine which apps need refactoring for cloud optimization
- Plan network and security configurations
This phase helps avoid surprises during migration and ensures a smooth transition.
Execution and Post-Migration Validation
Once planning is complete, execute the migration in phases. Start with non-critical applications to test the process.
- Use Azure Site Recovery for virtual machine migration
- Deploy apps using ARM templates or Terraform for consistency
- Validate functionality, performance, and security after migration
Post-migration, monitor the apps closely and optimize resource usage based on real-world performance.
Future Trends in Azure Apps Development
The landscape of cloud application development is evolving rapidly. Azure apps are at the forefront of innovation, embracing new technologies and development paradigms.
Rise of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, powered by Azure Functions, is gaining traction. It allows developers to run code in response to events without managing servers. This model is cost-effective and highly scalable.
- Execute functions in milliseconds
- Pay only for execution time
- Integrate with Event Grid, Blob Storage, and HTTP triggers
Serverless is ideal for microservices, image processing, and real-time data processing.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Azure apps are increasingly integrating AI capabilities through Azure Cognitive Services and Azure Machine Learning. Developers can add features like text analysis, speech recognition, and predictive analytics to their apps.
- Use pre-built AI models for vision and language
- Train custom models using Azure ML Studio
- Deploy AI models as REST APIs for app consumption
For instance, a customer support app can use sentiment analysis to prioritize urgent tickets.
What are Azure apps?
Azure apps are cloud-based applications hosted on Microsoft Azure, typically built using Azure App Service. They include web apps, mobile backends, APIs, and automated workflows, offering scalability, security, and integration with other Azure services.
How much do Azure apps cost?
Costs vary based on the pricing tier (Free to Premium), usage, and features. You can start with a free tier for testing and scale up as needed. Azure also offers cost calculators and reserved instances for savings.
Can I migrate my existing app to Azure?
Yes, Azure provides tools like Azure Migrate and Azure Site Recovery to help you assess, plan, and execute app migrations from on-premises or other clouds with minimal downtime.
Are Azure apps secure?
Absolutely. Azure apps benefit from Microsoft’s enterprise-grade security, including encryption, identity management, compliance certifications, and threat detection via Azure Security Center.
What is the difference between Azure App Service and Azure Functions?
Azure App Service is for hosting full web and mobile applications, while Azure Functions is a serverless platform for running small pieces of code (functions) in response to events, ideal for microservices and automation.
From scalability and security to AI integration and cost efficiency, Azure apps offer a comprehensive platform for modern application development. Whether you’re building a startup MVP or migrating enterprise systems, Azure provides the tools and infrastructure to succeed. With continuous innovation and global support, Azure apps are shaping the future of cloud computing.
Further Reading: